外贸独立站营销怎么做山东济南seo整站优化公司
嵌入式Linux应用开发-文件 IO
- 第四章 文件 IO
- 4.1 文件从哪来?
- 4.2 怎么访问文件?
- 4.2.1 通用的 IO 模型:open/read/write/lseek/close
- 4.2.2 不是通用的函数:ioctl/mmap
- 4.3 怎么知道这些函数的用法?
- 4.4 系统调用函数怎么进入内核?
- 4.5 内核的 sys_open、sys_read 会做什么?
第四章 文件 IO
参考书:

这 2 本书的内容类似,第一本对知识点有更细致的描述,适合初学者;第二本比较直接,一上来就是各种函数的介绍,适合当作字典,不懂时就去翻看一下。
做纯 Linux 应用的入,看这 2 本书就可以了,不需要学习我们的视频。我们的侧重于“嵌入式 Linux”。
在 Linux 系统中,一切都是“文件”:普通文件、驱动程序、网络通信等等。所有的操作,都是通过“文
件 IO”来操作的。所以,很有必要掌握文件操作的常用接口。
4.1 文件从哪来?

4.2 怎么访问文件?
4.2.1 通用的 IO 模型:open/read/write/lseek/close
使用 GIT 下载所有源码后,本节源码位于如下目录:
01_all_series_quickstart\
04_嵌入式 Linux 应用开发基础知识\source\06_fileio\copy.c
copy.c 源码如下:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h> /*
* ./copy 1.txt 2.txt
* argc = 3
* argv[0] = "./copy"
* argv[1] = "1.txt"
* argv[2] = "2.txt"
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{ int fd_old, fd_new; char buf[1024]; int len; /* 1. 判断参数 */ if (argc != 3) { printf("Usage: %s <old-file> <new-file>\n", argv[0]); return -1; } /* 2. 打开老文件 */ fd_old = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY); if (fd_old == -1) { printf("can not open file %s\n", argv[1]); return -1; } /* 3. 创建新文件 */ fd_new = open(argv[2], O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IWGRP | S_IROTH | S_IWOTH); if (fd_new == -1) { printf("can not creat file %s\n", argv[2]); return -1; } /* 4. 循环: 读老文件-写新文件 */ while ((len = read(fd_old, buf, 1024)) > 0) { if (write(fd_new, buf, len) != len) { printf("can not write %s\n", argv[2]); return -1; } } /* 5. 关闭文件 */ close(fd_old); close(fd_new); return 0;
} 本节源码完全可以在 Ubuntu 上测试,跟在 ARM 板上没什么不同。
执行以下命令编译、运行:
$ gcc -o copy copy.c
$ ./copy copy.c new.c 4.2.2 不是通用的函数:ioctl/mmap
使用 GIT 下载所有源码后,本节源码位于如下目录:
01_all_series_quickstart\
04_嵌入式 Linux 应用开发基础知识\source\06_fileio\copy_mmap.c
在 Linux 中,还可以把一个文件的所有内容映射到内存,然后直接读写内存即可读写文件。
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/mman.h> /*
* ./copy 1.txt 2.txt
* argc = 3
* argv[0] = "./copy"
* argv[1] = "1.txt"
* argv[2] = "2.txt"
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{ int fd_old, fd_new; struct stat stat; char *buf; /* 1. 判断参数 */ if (argc != 3) { printf("Usage: %s <old-file> <new-file>\n", argv[0]); return -1; } /* 2. 打开老文件 */ fd_old = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY); if (fd_old == -1) { printf("can not open file %s\n", argv[1]); return -1; } /* 3. 确定老文件的大小 */ if (fstat(fd_old, &stat) == -1) { printf("can not get stat of file %s\n", argv[1]); return -1; } /* 4. 映射老文件 */ buf = mmap(NULL, stat.st_size, PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, fd_old, 0); if (buf == MAP_FAILED) { printf("can not mmap file %s\n", argv[1]); return -1; } /* 5. 创建新文件 */ fd_new = open(argv[2], O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IWGRP | S_IROTH | S_IWOTH); if (fd_new == -1) { printf("can not creat file %s\n", argv[2]); return -1; } /* 6. 写新文件 */ if (write(fd_new, buf, stat.st_size) != stat.st_size) { printf("can not write %s\n", argv[2]); return -1; } /* 5. 关闭文件 */ close(fd_old); close(fd_new); return 0;
} 本节源码完全可以在 Ubuntu 上测试,跟在 ARM 板上没什么不同。
执行以下命令编译、运行:
$ gcc -o copy_mmap copy_mmap.c
$ ./copy_mmap copy_mmap.c new2.c
4.3 怎么知道这些函数的用法?
Linux 下有 3 大帮助方法:help、man、info。
想查看某个命令的用法时,比如查看 ls 命令的用法,可以执行:
ls --help
help 只能用于查看某个命令的用法,而 man 手册既可以查看命令的用法,还可以查看函数的详细介绍
等等。它含有 9 大分类,如下:
1 Executable programs or shell commands // 命令
2 System calls (functions provided by the kernel) // 系统调用,比如 man 2 open
3 Library calls (functions within program libraries) // 函数库调用
4 Special files (usually found in /dev) // 特殊文件, 比如 man 4 tty
5 File formats and conventions eg /etc/passwd // 文件格式和约定, 比如 man 5 passwd
6 Games // 游戏
7 Miscellaneous (including macro packages and conventions), e.g. man(7), groff(7) //杂
8 System administration commands (usually only for root) // 系统管理命令
9 Kernel routines [Non standard] // 内核例程
比如想查看 open 函数的用法时,可以直接执行“man open”,发现这不是想要内容时再执行“man 2
open”。
在 man 命令中可以及时按“h”查看帮助信息了解快捷键。常用的快捷键是:
f 往前翻一页
b 往后翻一页
/patten 往前搜
?patten 往后搜
就内容来说,info 手册比 man 手册编写得要更全面,但 man 手册使用起来更容易些。
以书来形容 info 手册和 man 手册的话,info 手册相当于一章,里面含有若干节,阅读时你需要掌握如
果从这一节跳到下一节;而 man 手册只相当于一节,阅读起来当然更容易。
就个人而言,我很少使用 info 命令。
可以直接执行“info”命令后,输入“H”查看它的快捷键,在 info 手册中,某一节被称为“node”,
常用的快捷键如下:
Up Move up one line.
Down Move down one line.
PgUp Scroll backward one screenful.
PgDn Scroll forward one screenful.
Home Go to the beginning of this node.
End Go to the end of this node. TAB Skip to the next hypertext link.
RET Follow the hypertext link under the cursor.
l Go back to the last node seen in this window.
[ Go to the previous node in the document.
] Go to the next node in the document.
p Go to the previous node on this level.
n Go to the next node on this level.
u Go up one level.
t Go to the top node of this document.
d Go to the main 'directory' node.
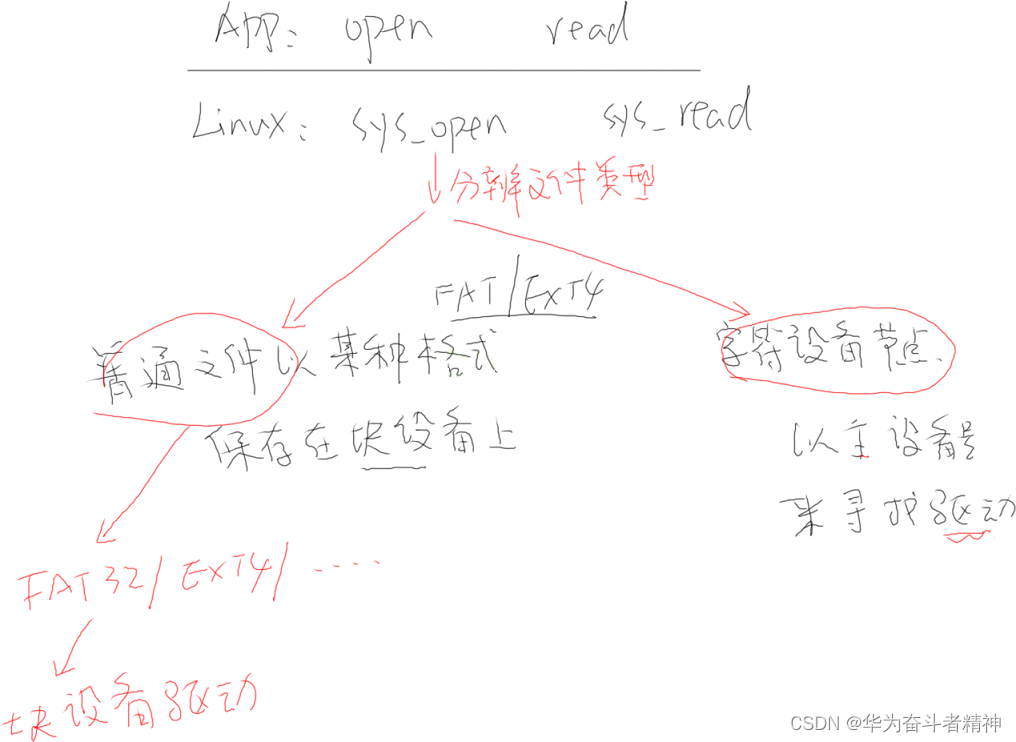
4.4 系统调用函数怎么进入内核?

4.5 内核的 sys_open、sys_read 会做什么?