做网站界面设计注意什么买域名
训练阶段
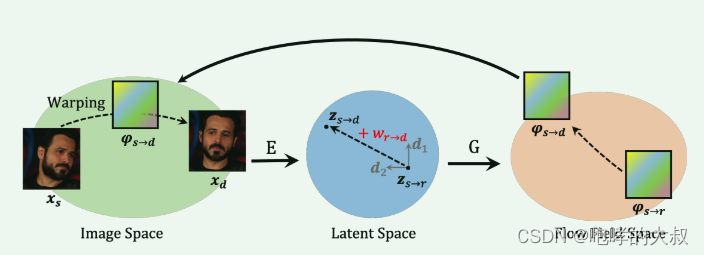
论文流程:
具体实现:
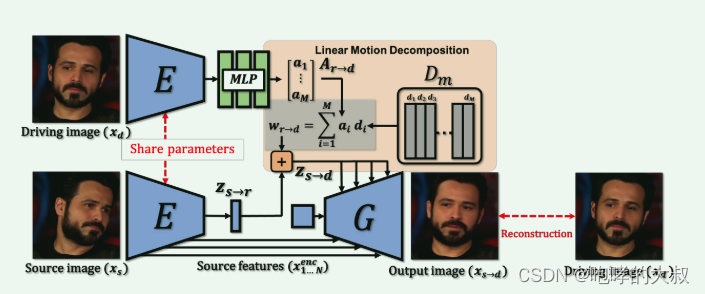
通过latent space传递运动信息,实现分两部分。
1)image space->latent space
将源图像映射到隐空间编码。X_s (source image )映射到编码Z_sr,通过W_rd方向上的变化,得到新的编码Z_sd。
X_s映射到编码Z_sr:通过编码器E映射成512维向量
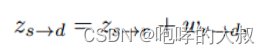
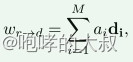
W_rd: driving image通过编码器E 映射成512维向量,然后通过MLP映射成20维视觉向量A_rd,与字典D中的向量结合得到w_rd,字典D包含了代表不同视觉变换的正交基,字典D是训练中学习得到的,每个向量有特定语意。
input_diag = torch.diag_embed(input) # alpha, diagonal matrix,20* 20对角矩阵
out = torch.matmul(input_diag, Q.T) #a_i*d_i
out = torch.sum(out, dim=1)
2)latent space->flow field space
通过编码器得到dense optical flow field,对图像进行warp
源图像特征与上一步得到的Z_sd逐级结合,上采样,得到输出图片X_sd。
代码中实现细节如下:
source和target id 相同时:
h_motion = [h_motion_target]
directions = self.direction(h_motion)
latent = wa + directions
source和target id 不相同时:
h_motion = [h_motion_target, h_motion_source, h_start]
h_start :driving的初始状态,默认需要与source同样的pose。
directions_target = self.direction(h_motion_target) #
latent = wa + (directions_target - directions_start) + directions_source
实际含义:
1)h_motion_:将图片通过share parameters编码成Z_sr(512维向量)
2)directions_: 将Zs_r映射成Zs_d(20维向量)
3)latent:source与target的相对/绝对位移信息
loss模块:
#criterion_vgg:vgg19特征层面的距离
#感知损失,计算img_target_recon与img_target原图做一个特征金字塔计算,然后送到vgg中,分别计算图像特征,最后两个特征张量做L1Loss
vgg_loss = self.criterion_vgg(img_target_recon, img_target).mean()
#图片像素层面的距离
l1_loss = F.l1_loss(img_target_recon, img_target)
#img_recon_pred为重演结果走了一遍判别器
#g_nonsaturating_loss=F.softplus(-img_recon_pred).mean()
#这种操作常见于生成对抗网络(GAN)的损失函数计算中,用于衡量假数据的质量,通常与真实数据的预测结果一起使用,以训练网络生成更接近真实数据分布的数据
gan_g_loss = self.g_nonsaturating_loss(img_recon_pred)g_loss = vgg_loss + l1_loss + gan_g_loss
其中vgg_loss与l1_loss,前提均需要source和target id 相同。
推断阶段
若id相同,采用与训练阶段范式一致的absolute transfer。
若id不同,则采用relative transfer,即将第一帧与驱动帧(target)的变化差异施加到源帧(source)上,并且要求源人脸和第一帧的pose要相似。
