网站建设 艺麟盛世营销型网站建设专家
前言
@RefeshScope这个注解想必大家都用过,在微服务配置中心的场景下经常出现,它可以用来刷新Bean中的属性配置,那么它是如何做到的呢?让我们来一步步揭开它神秘的面纱。
RefreshScope介绍
就是说我们在修改了bean属性的时候项目不需要重新启动,就可以拿到最新的值。
我们先来看下@RefreshScope的接口
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Scope("refresh")
@Documented
public @interface RefreshScope {/*** @see Scope#proxyMode()* @return proxy mode*///创建基于类的代理(使用 CGLIB)ScopedProxyMode proxyMode() default ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS;}可以看出其是一个复合注解,被标注了 @Scope(“refresh”),@RefreshScope 是scopeName="refresh"的 @Scope
我们来看下org.springframework.cloud.context.scope.refresh.RefreshScope类的关系图
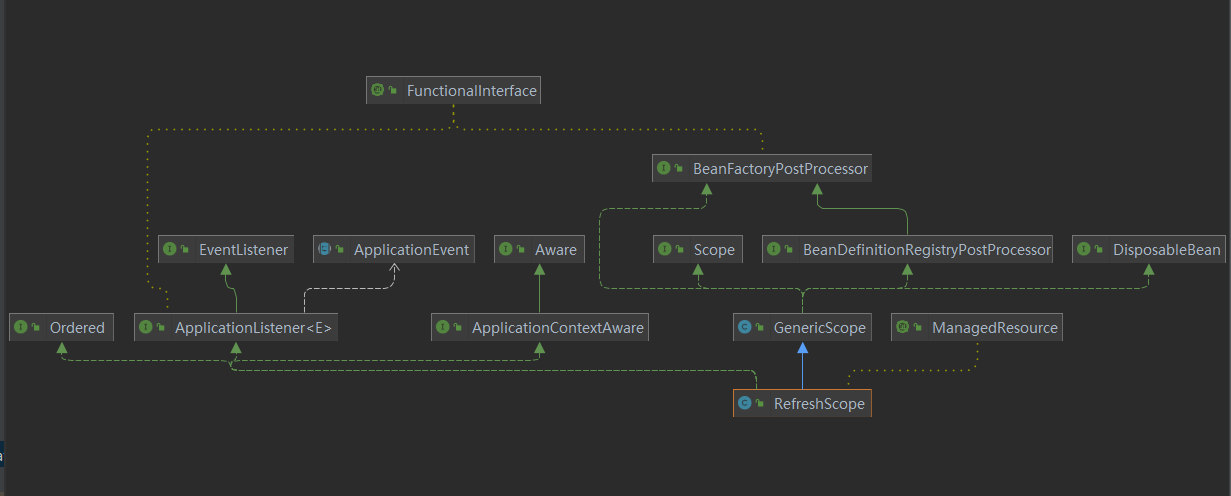
- Scope -> GenericScope -> RefreshScope
RefreshScope管理了Scope=Refresh的Bean的生命周期,提供了get(获取),refreshAll(刷新)、destory(销毁)等方法
源码解析
版本说明
<spring-boot.version>2.6.3</spring-boot.version><spring-cloud.version>2021.0.1</spring-cloud.version>
Bean创建过程
我们创建一个带@RefreshScope注解的类
@Data
@Component
@RefreshScope
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "test")
public class TestProperties {private String name ;}
启动项目进行debugger跟踪
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
AbstractApplicationContext#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法中
调用Bean Factory的后置处理器,从上面的类图中我们可以看到RefreshScope就是一个BeanFactoryPostProcessors
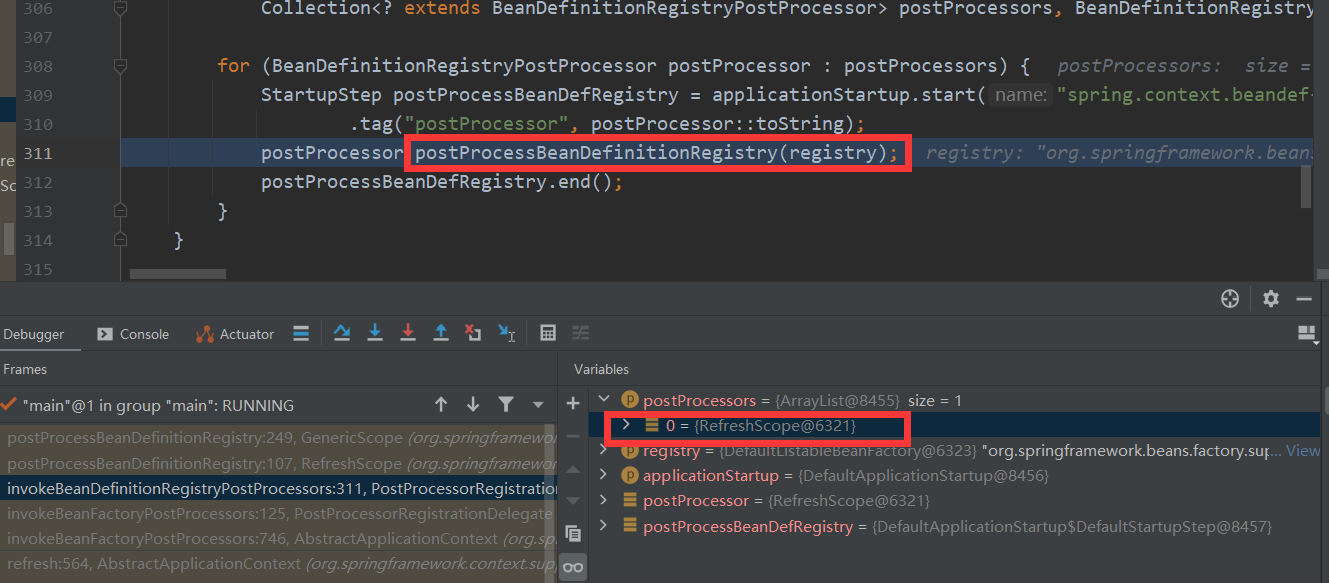
然后调用父类GenericScope的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法
该方法遍历所有的bean定义 如果当前的bean的scope为refresh,那么就把当前的bean设置为 LockedScopedProxyFactoryBean的代理对象。
@RefreshScope标注的类还有一个特点:会使用代理对象并进行延迟加载。我们来看一下postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法
@RefreshScope 注解的 bean,除了会生成一个beanName的 bean,同时会生成 scopedTarget.beanName的 bean
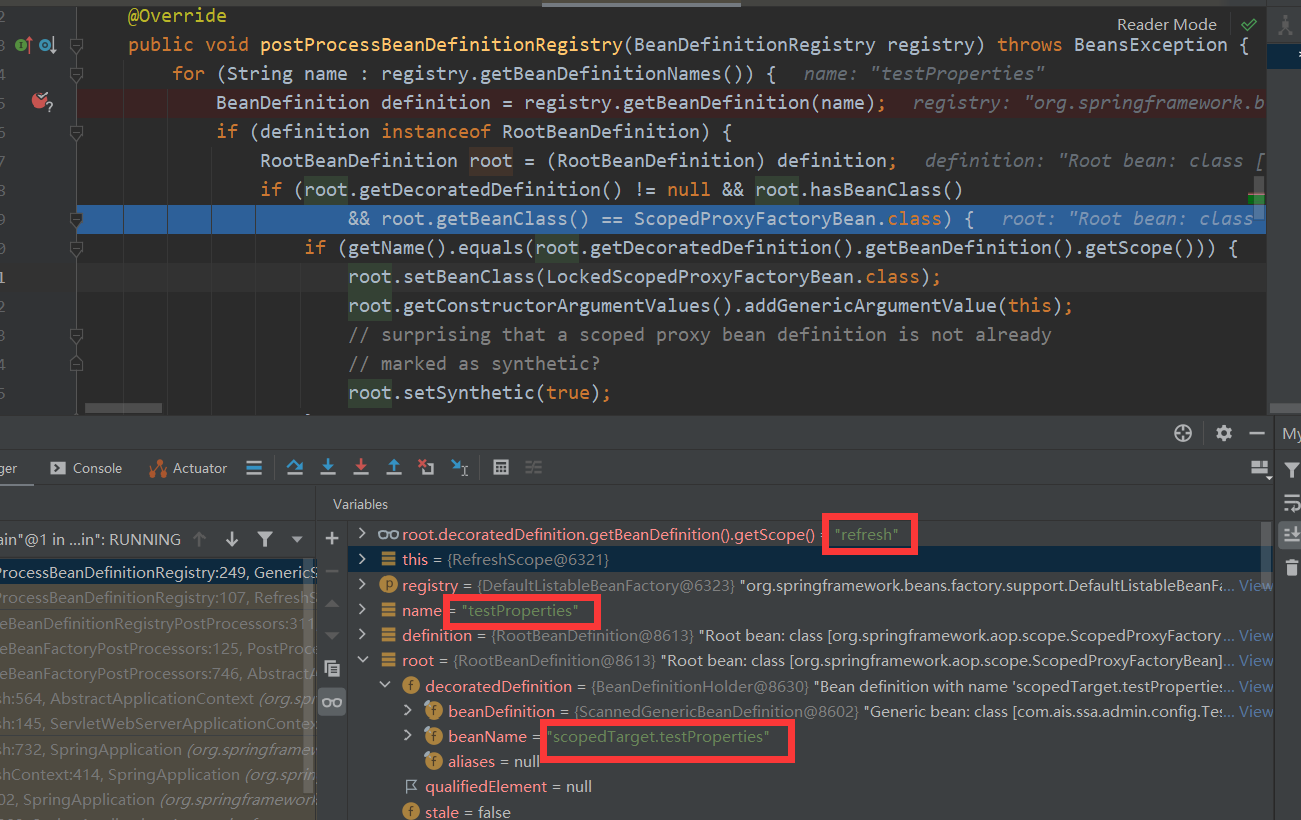
所以如果有@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate 注解的 bean,就不能在使用@RefreshScope的注解了。因为@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate全局只能有一个此类型的 bean
RefreshScope还会监听一个ContextRefreshedEvent,该事件会在ApplicationContext初始化或者refreshed时触发
ContextRefreshedEvent事件
AbstractApplicationContext#finishRefresh方法中
// 上下文刷新事件publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
我们来看一下RefreshScope中的代码:
@Overridepublic void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {start(event);}public void start(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {if (event.getApplicationContext() == this.context && this.eager && this.registry != null) {eagerlyInitialize();}}private void eagerlyInitialize() {for (String name : this.context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {BeanDefinition definition = this.registry.getBeanDefinition(name);if (this.getName().equals(definition.getScope()) && !definition.isLazyInit()) {Object bean = this.context.getBean(name);if (bean != null) {bean.getClass();}}}}
如果这个bean的scope = refresh的话就会去执行getBean方法,我们可以看到bean的名字为scopedTarget.testProperties这是一个被代理过的bean
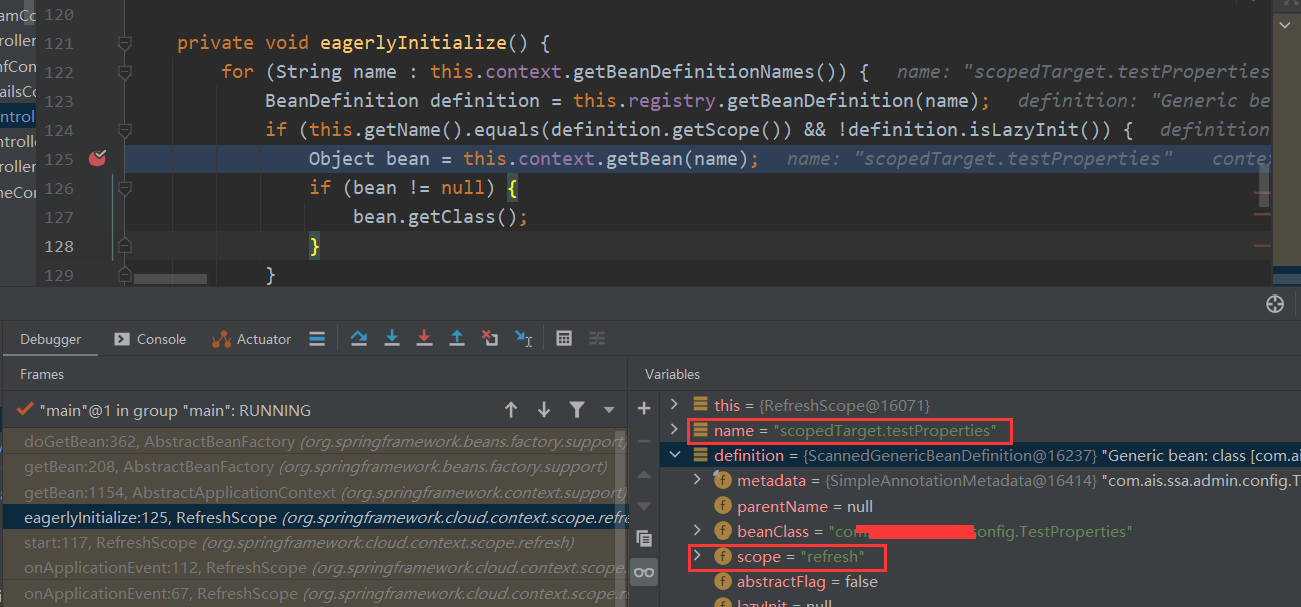
doGetBean
上面的this.context.getBean(name)中会使用BeanFactory的doGetBean方法创建Bean,不同scope有不同的创建方式:
protected <T> T doGetBean(String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)throws BeansException {String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);Object beanInstance;...// 创建单例beanif (mbd.isSingleton()) {sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {try {return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);}catch (BeansException ex) {// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.destroySingleton(beanName);throw ex;}});beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);}// 创建原型beanelse if (mbd.isPrototype()) {// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.Object prototypeInstance = null;try {beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);}finally {afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);}beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);}// Scope 类型创建beanelse {String scopeName = mbd.getScope();if (!StringUtils.hasLength(scopeName)) {throw new IllegalStateException("No scope name defined for bean '" + beanName + "'");}Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);if (scope == null) {throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");}try {//使用RefreshScope父类的get方法,然后使用ConcurrentMap缓存下来Object scopedInstance =scope.get(beanName, () -> {//把Bean信息存储到ThreadLocal变量中beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);try {return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);}finally {//把Bean信息从ThreadLocal变量中移除afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);}});beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);}catch (IllegalStateException ex) {throw new ScopeNotActiveException(beanName, scopeName, ex);}}}catch (BeansException ex) {beanCreation.tag("exception", ex.getClass().toString());beanCreation.tag("message", String.valueOf(ex.getMessage()));cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);throw ex;}finally {beanCreation.end();}}return adaptBeanInstance(name, beanInstance, requiredType);}
- 单例和原型的Bean都是硬编码写在代码里面的
- 除了单例和原型Bean,其他Scope是由Scope对象处理的
- 使用RefreshScope父类的get方法,然后使用ConcurrentMap缓存下来
然后执行createBean创建Bean,创建Bean还是由IOC来做(createBean方法),但是获取Bean,都由RefreshScope对象的get方法去获取,其get方法在父类GenericScope中。GenericScope 实现了 Scope 最重要的 get(String name, ObjectFactory objectFactory) 方法,在GenericScope 里面 包装了一个内部类 BeanLifecycleWrapperCache。来对加了 @RefreshScope 创建的对象进行缓存,使其在不刷新时获取的都是同一个对象。(这里你可以把 BeanLifecycleWrapperCache 想象成为一个大Map 缓存了所有@RefreshScope 标注的对象)
GenericScope中get方法
@Overridepublic Object get(String name, ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory) {BeanLifecycleWrapper value = this.cache.put(name, new BeanLifecycleWrapper(name, objectFactory));this.locks.putIfAbsent(name, new ReentrantReadWriteLock());try {return value.getBean();}catch (RuntimeException e) {this.errors.put(name, e);throw e;}}public Object getBean() {if (this.bean == null) {synchronized (this.name) {if (this.bean == null) {this.bean = this.objectFactory.getObject();}}}return this.bean;}
BeanLifecycleWrapper这个是@RefreshScope标记bean的一个包装类,会被存储到缓存里,在这里取不到值的话就会从objectFactory里去拿,也就是重新创建一个去执行doCreateBean方法
动态刷新Bean的配置变量值
当配置中心刷新配置之后,有两种方式可以动态刷新Bean的配置变量值,(SpringCloud-Bus还是Nacos差不多都是这么实现的)
- 向上下文发布一个RefreshEvent事件
- Http访问/refresh这个EndPoint (RefreshEndpoint)
RefreshEventListener 监听器
当我们发布一个RefreshEvent事件的时候,RefreshEventListener就会监听到,然后调用handle处理
@Overridepublic void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {if (event instanceof ApplicationReadyEvent) {handle((ApplicationReadyEvent) event);}else if (event instanceof RefreshEvent) {handle((RefreshEvent) event);}}...public void handle(RefreshEvent event) {if (this.ready.get()) { // don't handle events before app is readylog.debug("Event received " + event.getEventDesc());//调用ContextRefresher的refresh方法Set<String> keys = this.refresh.refresh();log.info("Refresh keys changed: " + keys);}}
ContextRefresher
调用refresh方法
public synchronized Set<String> refresh() {Set<String> keys = refreshEnvironment();// RefreshScope调用刷新方法this.scope.refreshAll();return keys;}public synchronized Set<String> refreshEnvironment() {//把原来的配置都读取出来放到map里面Map<String, Object> before = extract(this.context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources());//更新环境updateEnvironment();//获取新老之间有差异的属性源key集合Set<String> keys = changes(before, extract(this.context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources())).keySet();//发布EnvironmentChangeEvent事件,这个事件是ConfigurationPropertiesRebinder监听的this.context.publishEvent(new EnvironmentChangeEvent(this.context, keys));return keys;}
updateEnvironment(更新环境)
- 先拷贝出基础的环境属性
- 通过SpringApplicationBuilder构建了一个简单的SpringBoot启动程序
- 这里面会添加两个监听器分别为:BootstrapApplicationListener与ConfigFileApplicationListener,BootstrapApplicationListener是引导程序的核心监听器,而ConfigFileApplicationListener主要就是读取配置文件的
- 然后调用run方法启动,就是springboot的run方法。使用非WEB的方式启动
- 然后读取最新的配置出来遍历,如果不是基础属性配置的环境并且老的环境和新的环境有一样的就替换成新的环境
@Overrideprotected void updateEnvironment() {addConfigFilesToEnvironment();}/* For testing. */ ConfigurableApplicationContext addConfigFilesToEnvironment() {ConfigurableApplicationContext capture = null;try {//拷贝出基础的环境环境属性,如系统环境变量,Java的属性StandardEnvironment environment = copyEnvironment(getContext().getEnvironment());Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("spring.jmx.enabled", false);map.put("spring.main.sources", "");// gh-678 without this apps with this property set to REACTIVE or SERVLET failmap.put("spring.main.web-application-type", "NONE");map.put(BOOTSTRAP_ENABLED_PROPERTY, Boolean.TRUE.toString());environment.getPropertySources().addFirst(new MapPropertySource(REFRESH_ARGS_PROPERTY_SOURCE, map));SpringApplicationBuilder builder = new SpringApplicationBuilder(Empty.class).bannerMode(Banner.Mode.OFF).web(WebApplicationType.NONE).environment(environment);// Just the listeners that affect the environment (e.g. excluding logging// listener because it has side effects)builder.application().setListeners(Arrays.asList(new BootstrapApplicationListener(), new BootstrapConfigFileApplicationListener()));capture = builder.run();if (environment.getPropertySources().contains(REFRESH_ARGS_PROPERTY_SOURCE)) {environment.getPropertySources().remove(REFRESH_ARGS_PROPERTY_SOURCE);}//老的配置MutablePropertySources target = getContext().getEnvironment().getPropertySources();String targetName = null;//遍历新配置for (PropertySource<?> source : environment.getPropertySources()) {String name = source.getName();if (target.contains(name)) {targetName = name;}//老的环境不包含基础的配置if (!this.standardSources.contains(name)) {//老的环境里面有新环境的配置if (target.contains(name)) {//替换target.replace(name, source);}else {if (targetName != null) {target.addAfter(targetName, source);// update targetName to preserve orderingtargetName = name;}else {// targetName was null so we are at the start of the listtarget.addFirst(source);targetName = name;}}}}}finally {ConfigurableApplicationContext closeable = capture;while (closeable != null) {try {closeable.close();}catch (Exception e) {// Ignore;}if (closeable.getParent() instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext) {closeable = (ConfigurableApplicationContext) closeable.getParent();}else {break;}}}return capture;}
changes(新老键值比较)
找出改变过的值放到result里面
private Map<String, Object> changes(Map<String, Object> before, Map<String, Object> after) {Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<String, Object>();for (String key : before.keySet()) {if (!after.containsKey(key)) {result.put(key, null);}else if (!equal(before.get(key), after.get(key))) {result.put(key, after.get(key));}}for (String key : after.keySet()) {if (!before.containsKey(key)) {result.put(key, after.get(key));}}return result;}
EnvironmentChangeEvent事件
由ConfigurationPropertiesRebinder来处理这个事件。调用rebind方法进行配置重新加载,rebind方法实际上就是先销毁再去创建Bean。这里会遍历所有带@ConfigurationProperties注解的Bean,但是并不包含有@RefreshScope注解的。
destroyBean:如果这个Bean实现了DisposableBean接口,就是执行destroy方法。或者是有实现AutoCloseable接口就进行资源关闭操作
initializeBean:bean初始化的操作
@Overridepublic void onApplicationEvent(EnvironmentChangeEvent event) {if (this.applicationContext.equals(event.getSource())// Backwards compatible|| event.getKeys().equals(event.getSource())) {rebind();}}@ManagedOperationpublic void rebind() {this.errors.clear();for (String name : this.beans.getBeanNames()) {rebind(name);}}@ManagedOperationpublic boolean rebind(String name) {if (!this.beans.getBeanNames().contains(name)) {return false;}if (this.applicationContext != null) {try {Object bean = this.applicationContext.getBean(name);if (AopUtils.isAopProxy(bean)) {bean = ProxyUtils.getTargetObject(bean);}if (bean != null) {// TODO: determine a more general approach to fix this.// see https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-commons/issues/571if (getNeverRefreshable().contains(bean.getClass().getName())) {return false; // ignore}this.applicationContext.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory().destroyBean(bean);this.applicationContext.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory().initializeBean(bean, name);return true;}}catch (RuntimeException e) {this.errors.put(name, e);throw e;}catch (Exception e) {this.errors.put(name, e);throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot rebind to " + name, e);}}return false;}
ContextRefresher#refreshAll
发布事件完以后就执行 RefreshScope中的refreshAll
public void refreshAll() {super.destroy();this.context.publishEvent(new RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent());}
super.destroy()调用父类的destroy方法。这里把cache缓存给清理掉。
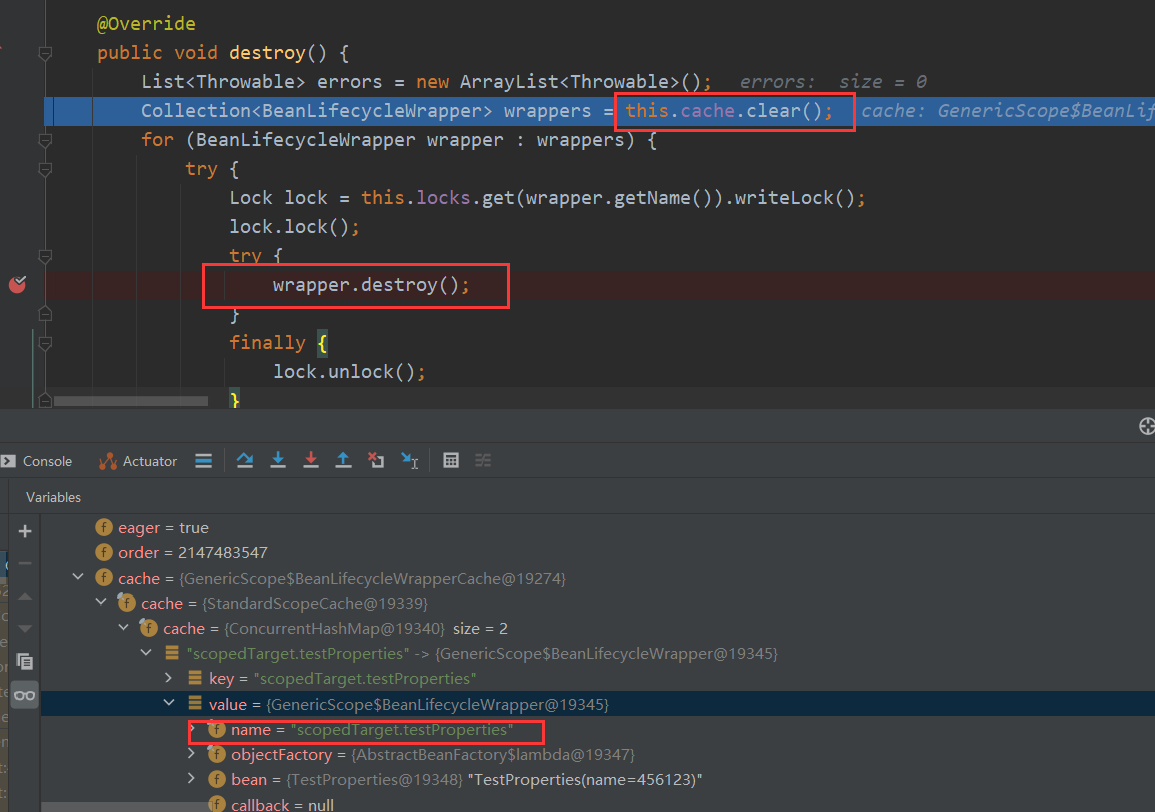
wrapper.destroy();
缓存中的bean清除了,但是这些bean还需要销毁。
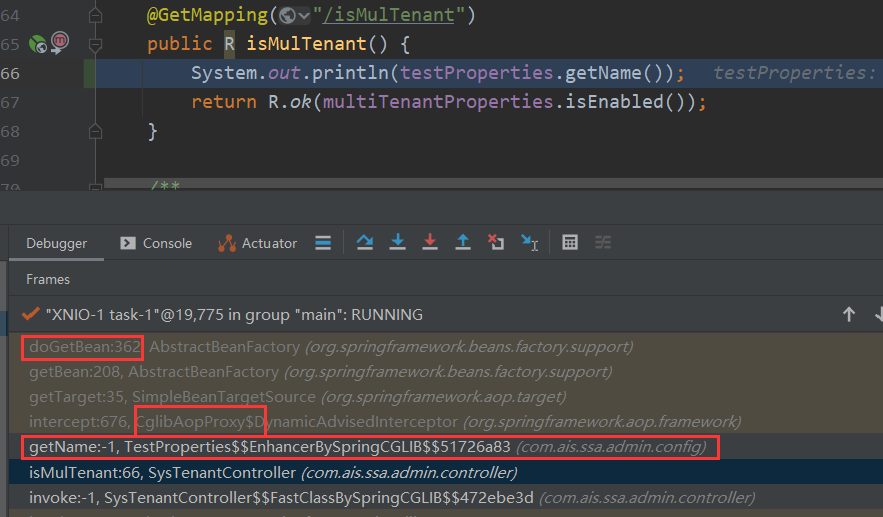
public void destroy() {if (this.callback == null) {return;}synchronized (this.name) {Runnable callback = this.callback;if (callback != null) {callback.run();}this.callback = null;this.bean = null;}}然后当我们项目中有使用到被@RefreshScope注释的Bean的时候,在doGetBean方法中从GenericScope中的cache缓存中获取不到的话就会重新去创建Bean。这样获取到的就是最新的值了。
获取类的中属性时,会重新调用doGetBean的
总结
- 被@RefreshScope标注的Bean在创建的时候是会生产一个代理对象
- 当发布RefreshEvent事件时,会调用ContextRefresher#refresh方法,该方法会记录当前的环境,然后构建一个非web的SpringApplicationBuilder并执行其run方法。
- 通过新旧环境的比较找出修改过的属性。changes操作来变更已有的PropertySource。
- 通过EnvironmentChangeEvent事件把缓存中清除
- 再次获取对象的时候重新创建,从新的属性环境中读取最新值
