在线下单网站怎么做it培训机构口碑排名
一、高性能
-
使用sync.pool解决频繁创建的context对象,在百万并发的场景下能大大提供访问性能和减少GC
// ServeHTTP conforms to the http.Handler interface. // 每次的http请求都会从sync.pool中获取context,用完之后归还到pool中 func (engine *Engine) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {c := engine.pool.Get().(*Context)c.writermem.reset(w) //重置 responsewriterc.Request = reqc.reset() //重置使用过的context各个属性engine.handleHTTPRequest(c)engine.pool.Put(c) }// 这里给pool指定了一个创建新对象的函数,注意不是所有的请求共用一个context,context在高并发场景下可能会分配多个,但是远远小于并发协程数量。 sync.pool.new是可能并发调用的,所以内部的逻辑需要保障线程安全 func New(opts ...OptionFunc) *Engine {... engine.RouterGroup.engine = engineengine.pool.New = func() any {return engine.allocateContext(engine.maxParams)}return engine.With(opts...) }//每次http请求都需要分配一个context,这个初始context初始化了两个数组的最大容量 func (engine *Engine) allocateContext(maxParams uint16) *Context {v := make(Params, 0, maxParams)skippedNodes := make([]skippedNode, 0, engine.maxSections)return &Context{engine: engine, params: &v, skippedNodes: &skippedNodes} } -
前缀树路由(类似httprouter的路由,提升性能近40倍)
gin在v1.0版本开始放弃了
github.com/julienschmidt/httprouter,重新实现了一套路由;对比gin新实现的路由基本上采用了httprouter的逻辑,但是和框架结合的更加完整,比如说把httprouter中router的能力提到了engine中。 -
json序列化优化
gin提供了四种可选的json序列化方式,默认情况下会使用encoding/json
/github.com/gin-gonic/gin@v1.10.0/internal/json-- go_json.go ("github.com/goccy/go-json")-- json.go ("encoding/json")-- jsoniter.go ("github.com/json-iterator/go")-- sonic.go ("github.com/bytedance/sonic")需要在编译期间指定tag来决定使用哪种序列化工具
go run -tags={go_json|jsoniter|sonic|(不指定默认encoding)} main.go通过一个简单的基准测试看看哪种json序列化效率更高
package ganimport ("encoding/json"sonicjson "github.com/bytedance/sonic"gojson "github.com/goccy/go-json"itjson "github.com/json-iterator/go""testing" )func BenchmarkJson(b *testing.B) {jsonStr := `{"name":"zhangsan","age":18,"address":"beijing"}`m := &map[string]interface{}{}for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {json.Unmarshal([]byte(jsonStr), m)json.Marshal(m)} }func BenchmarkGOJson(b *testing.B) {jsonStr := `{"name":"zhangsan","age":18,"address":"beijing"}`m := &map[string]interface{}{}for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {gojson.Unmarshal([]byte(jsonStr), m)gojson.Marshal(m)} }func BenchmarkItJson(b *testing.B) {m := &map[string]interface{}{}jsonStr := `{"name":"zhangsan","age":18,"address":"beijing"}`for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {itjson.Unmarshal([]byte(jsonStr), m)itjson.Marshal(m)} }func BenchmarkSonicJson(b *testing.B) {m := &map[string]interface{}{}jsonStr := `{"name":"zhangsan","age":18,"address":"beijing"}`for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {sonicjson.Unmarshal([]byte(jsonStr), m)sonicjson.Marshal(m)} }测试结果: sonic > go_json > json_iterator > encoding
$ go test -bench='Json$' -benchtime=5s -benchmem . goos: windows goarch: amd64 pkg: gan cpu: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-10400 CPU @ 2.90GHz BenchmarkJson-12 2632854 2260 ns/op 616 B/op 24 allocs/op BenchmarkGOJson-12 5226374 1142 ns/op 248 B/op 11 allocs/op BenchmarkItJson-12 4811112 1260 ns/op 400 B/op 19 allocs/op BenchmarkSonicJson-12 6616218 913.0 ns/op 333 B/op 10 allocs/op PASS ok gan 30.313s
二、基于前缀树的路由设计
-
go语言中原生net/http包在负载路由下的缺陷
动态路由:缺少例如hello/:name,hello/*这类的规则。
鉴权:没有分组/统一鉴权的能力,需要在每个路由映射的handler中实现。 -
http请求怎么进入的gin的处理逻辑中去的?
-
gin框架中调用了net/http包,监听address,请求都会进入顶层路由,也就是engine结构实现的ServeHTTP函数中
func (engine *Engine) Run(addr ...string) (err error) {......debugPrint("Listening and serving HTTP on %s\n", address)err = http.ListenAndServe(address, engine.Handler())return } func (engine *Engine) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {......engine.handleHTTPRequest(c)...... } -
在engine.handleHTTPRequest© 中,根据request中的path,在路由表中获取路由对应的handler然执行
func (engine *Engine) handleHTTPRequest(c *Context) {httpMethod := c.Request.MethodrPath := c.Request.URL.Path......// Find root of the tree for the given HTTP methodt := engine.treesfor i, tl := 0, len(t); i < tl; i++ {if t[i].method != httpMethod {continue}root := t[i].root// Find route in treevalue := root.getValue(rPath, c.params, c.skippedNodes, unescape)if value.params != nil {c.Params = *value.params}if value.handlers != nil {c.handlers = value.handlersc.fullPath = value.fullPathc.Next() //最终执行的handlerc.writermem.WriteHeaderNow()return}......} }
-
-
路由的注册和匹配
-
Engine继承了RouterGroup的能力,当我们注册handler时,或者在分组路由下去注册handler时,其实都是调用的RouterGroup的能力
type Engine struct {RouterGroup...... } -
RouterGroup中保留了一个Engine指针,最终的路由是注册到了Engine中的路由表中,这个路由表没有设计在RouterGroup中,保证了RouterGroup的职责单一性,也就是只做路由分组。
func (group *RouterGroup) handle(httpMethod, relativePath string, handlers HandlersChain) IRoutes {......group.engine.addRoute(httpMethod, absolutePath, handlers)return group.returnObj() } -
Engine中保存了一个methodTree对象,这个就是路由表,是一个树状结构
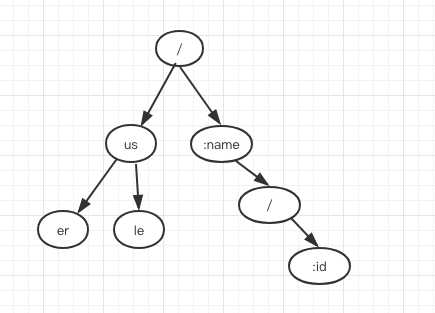
type methodTree struct {method stringroot *node }type node struct {path stringindices stringwildChild boolnType nodeTypepriority uint32children []*node // child nodes, at most 1 :param style node at the end of the arrayhandlers HandlersChainfullPath string }type methodTrees []methodTree
-
三、中间件执行流程
-
中间件执行链路
-
中间件保存在GroupRouter中
func (group *RouterGroup) Use(middleware ...HandlerFunc) IRoutes {group.Handlers = append(group.Handlers, middleware...)return group.returnObj() } -
每声明一次分组,都会将handler进行一次合并
func (group *RouterGroup) Group(relativePath string, handlers ...HandlerFunc) *RouterGroup {return &RouterGroup{Handlers: group.combineHandlers(handlers), //合并中间处理链路basePath: group.calculateAbsolutePath(relativePath),engine: group.engine,} } -
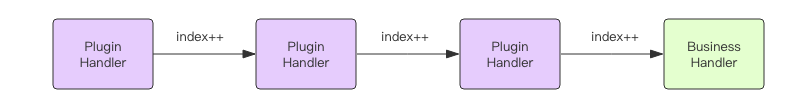
以上只是将中间件合并成了一条链路,最终的业务逻辑会在执行GET.POST等请求方法时,拼接到执行链路末端
func (group *RouterGroup) handle(httpMethod, relativePath string, handlers HandlersChain) IRoutes {absolutePath := group.calculateAbsolutePath(relativePath)handlers = group.combineHandlers(handlers) //这里参数的handlers是业务逻辑,合并到链路末尾。group.engine.addRoute(httpMethod, absolutePath, handlers)return group.returnObj() } -
最终效果
-
-
前置处理和后置处理
-
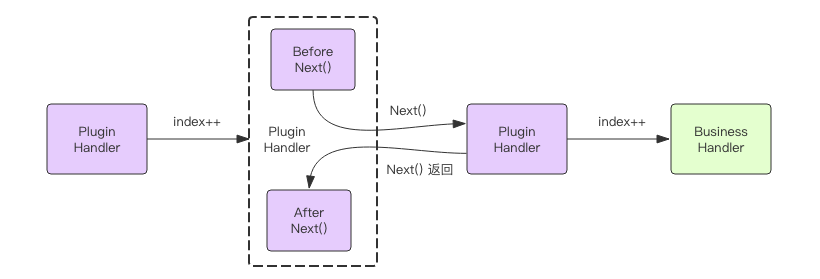
假设需要对一段业务逻辑采集它的执行耗时,一般我们需要在执行逻辑前声明一个时间点,执行完后再用当前时间减去执行前的时间得到耗时。
-
在gin中的实现方式是通过context的next方法去实现的,结合上面的流程,在中间件中每声明一次next,执行链会先去执行下一个handler,最终的效果应该是ABBA方式的执行。
func (c *Context) Next() {c.index++for c.index < int8(len(c.handlers)) {c.handlers[c.index](c)c.index++} }
-
其他:
Gin的核心特性
- 高性能:Gin的HTTP请求处理速度极快,能够支持大量的并发连接(gin并不是基准测试中最快的框架,但是相对较快,简单好用,用户体量大)
- 简单易用:Gin的API设计直观,使得开发者可以快速上手并构建应用。
- 中间件支持:Gin允许开发者通过中间件来扩展其功能,这为构建复杂的Web应用提供了可能。
- 路由和参数绑定:Gin提供了强大的路由功能,支持参数绑定,使得URL处理更加灵活。
- 数据渲染:Gin支持多种数据渲染方式,包括JSON、XML、HTML等,方便开发者根据需求选择合适的输出格式。
